Marketing Management
"Good Marketing is no accident,but a result of careful planning and execution using state-of-art tools and techniques."
"Good Marketing is no accident,but a result of careful planning and execution using state-of-art tools and techniques."
•The importance of Marketing:
- All business functions won’t really matter without sufficient demand for products & services so the firm can make profit.
•Marketers must decide:
•what features to design in to a new product or service.
•What price to set.
•Where to sell products or offer services.
•How much to spend on advertising, sales, the internet, or mobile marketing.
They must make those decisions in an internet-fueled environment where all forces change rapidly.
MARKETING MANAGEMENT
KOTLER KELLER_ GLOBAL EDITION
KOTLER KELLER_ GLOBAL EDITION
Prepared By,
Sema Farhoud
MBA-Marketing
8 Demand states are possible
How some top firms drive Business
•OfficeMax,•Promoted a new line of products by professional organizer (Peter Walsh) wit web videos & in-store events featuring local experts demonstrating his OfficeMax branded organizing.•eBay,•Promoted its “let’s make a daily deal” holiday promotion by recreating the famous 1970s TV game show “let’s make a deal”•Johnson & Johnson,•Launched babycenter.com to help new parents. Its success is thought to have contributed to subscription slumps experienced by parenting magazine.
The Scope of Marketing
•What is Marketing?
•Marketing is about identifying & meeting human & social needs.
One of the shortest good definitions of Marketing :”Meeting needs Profitably”
•EX:
*eBay, when eBay recognized that people were unable to locate some of the items they desired most, it created an online auction.
*IKEA, when IKEA noticed that people wanted good furnishings at substantially lower prices, it created Knockdown furniture.
The American Marketing Association Formal Definition
“Marketing is the activity, set of institutions, and process for clearing, communicating, delivering, and exchanging offerings that have value for customers, clients, partners, and society at large.”
Marketing Management
“The Art & science of choosing target markets & getting, keeping,& growing customers through creating, delivering, & communicating superior customer value.”
(Marketing is to deliver a higher standard of living.)
•EX:
*Nintendo, when Nintendo designed its Wii game system
*Canon, when launched its ELPH digital camera line
*Toyota, when introduced its Prius hybrid automobile
“these manufacturers were swamped wit orders, because they had designed the right product, based on doing careful marketing homework.”
MARKETING MANAGEMENT
KOTLER KELLER_ GLOBAL EDITION
KOTLER KELLER_ GLOBAL EDITION
Prepared By,
Sema Farhoud
MBA-Marketing
Who Markets?
Marketers & Prospects
A marketer is s.one who seeks a response, attention, a purchase, a vote, a donation – from another party, called the prospect.
•If two parties are seeking to sell s.thing to each other we call both Marketers.
•As production & logistics professionals are responsible for supply management, marketers are responsible for Demand Management.
8 Demand states are possible
1.Negative Demand, consumers hate the product & even pay to avoid it
2.Nonexistent Demand, consumers are unaware of or uninterested in the product
3.Declining Demand, consumers begin to buy the product less frequently or not at all.
4.Full Demand, consumers are adequately buying all products put into the market place.
5.Overfull Demand, more consumers would like to buy the product than can be satisfied.
6.Irregular Demand, consumer purchase vary on seasonal, monthly, weekly, daily, or even hourly.
7.Latent Demand, consumers may share a strong need that cannot be satisfied by an existing product.
8.Unwholesome Demand, consumers may be attached to products that have undesirable social consequences.
Markets
•Economists describe a Market as a collection of buyers & sellers who transact over a particular product or product class.
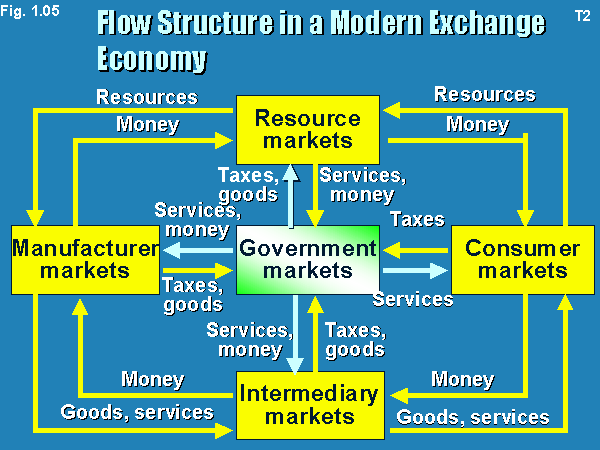
•5 basic Markets & their connecting flow,
•Manufacturers Go to Resource markets – Raw material markets, Labor markets , Money markets – BUY resources & Turn them into goods & services, and Sell finished products to Intermediaries , who Sell them to Consumers. Consumers Sell their labor & receive Money with each they pay for goods & services.
The Government collects Tax revenues to Buy goods from Resources, Manufacturers, & intermediary markets & Uses these goods & services to provide public services.
Structure of flows in a modern exchange economy
Key consumer Markets
•The key Customer Markets
1.Consumer .. Companies sell mass consumer goods & services spend a great deal of time establishing a strong brand image by developing a superior product & packaging. ensuring its availability, & backing it with engaging communications & reliable service.
2.Business .. Companies selling business goods & services often face well-informed professional buyers skilled at evaluating competitive offerings. Marketers must demonstrate how their products well help achieve higher revenue or lower cost.
3.Global .. Companies in that market must decide which countries to enter, how to enter each (as exporter, licenser, joint venture partner, contract manufacturer, or solo manufacturer. How to adapt product features, how to price, how to design communications for different cultures.
4.Non profit & governmental markets .. Companies selling to non profit org. with limited purchasing power such as univ. governmental agencies , … need to price carefully. Much government purchasing calls for bids.
Marketplace , Marketspace , & METAmarket




No comments:
Post a Comment
Add your comment here